EV Tire Technologies Hiring Demands
Electric vehicles (EVs) are reshaping the automotive ecosystem and EV tire technologies are a critical frontier in that transformation. As EVs bring greater torque, weight, and demands for efficiency and connectivity, tires must evolve. This shift is creating new roles, new skills, and fresh challenges in hiring for the U.S. tire industry.
In this article, you’ll get:
- A deep dive into the landscape of EV tire technologies
- Why these tech shifts drive specific hiring demands
- Key roles, compensation benchmarks, and skills in demand
- Challenges employers face in hiring for EV tire technology
- Best practices to attract, evaluate, and retain top talent
- How TireTalent (and your recruiting approach) can help
Read on, and you’ll gain clarity on which technical domains to prioritize, how to recruit smartly, and what the ROI of staffing right in this space looks like.

1. The Evolution: What Makes an EV Tire Different?
To understand hiring needs, first understand how EV tires differ from conventional ones:
Key Technological Shifts
- Low Rolling Resistance & High Efficiency
EVs are heavy (battery weight), and energy efficiency is paramount. Tires with low rolling resistance help maximize range. Manufacturers use advanced compounds, silica blends, optimized tread patterns, and stiffer sidewalls. - Noise & NVH (Noise, Vibration, Harshness) Control
Because EVs lack engine noise, tire noise becomes more audible. EV tire technology must reduce road noise and vibration. - Durability under High Torque
EVs deliver instant torque, which creates high shear forces. Tires must resist wear, heat, and deformation under high torque and heavier loads. - Smart & Sensor-Embedded Tires
Many OEMs and tire makers are embedding sensors (temperature, pressure, wear) and connectivity in tires to support predictive maintenance, safety integration, and real-time feedback. - Sustainability, Recyclability, & Material Innovation
Use of more sustainable materials, bio-based rubbers, recycled rubber, and closed-loop manufacturing is rising. Tires must meet regulatory & consumer sustainability demands. - Charge / Heat Management
EV tires must dissipate heat effectively and maintain performance under thermal stress, especially for high-speed driving or fast charging cycles. Some designs incorporate advanced heat-conducting materials.
These technological demands mean that tomorrow’s tire roles will require skillsets beyond traditional rubber chemistry blending materials science, sensors, electronics, data, and systems thinking.
2. Market Growth & Demand Signals
Understanding demand helps validate which roles will be in high pressure.
- The global EV tire market is projected to grow rapidly. For example, one analysis forecasts the EV tire segment to reach $46.2 billion by 2027, up from ~$15.6 billion in 2022 (CAGR ~24.3%)
- In North America, the EV tire market is also growing, driven by rising EV adoption and stricter efficiency requirements.
- Tire makers are continuing to invest heavily in EV-specific designs to accommodate new performance, efficiency, and durability requirements.
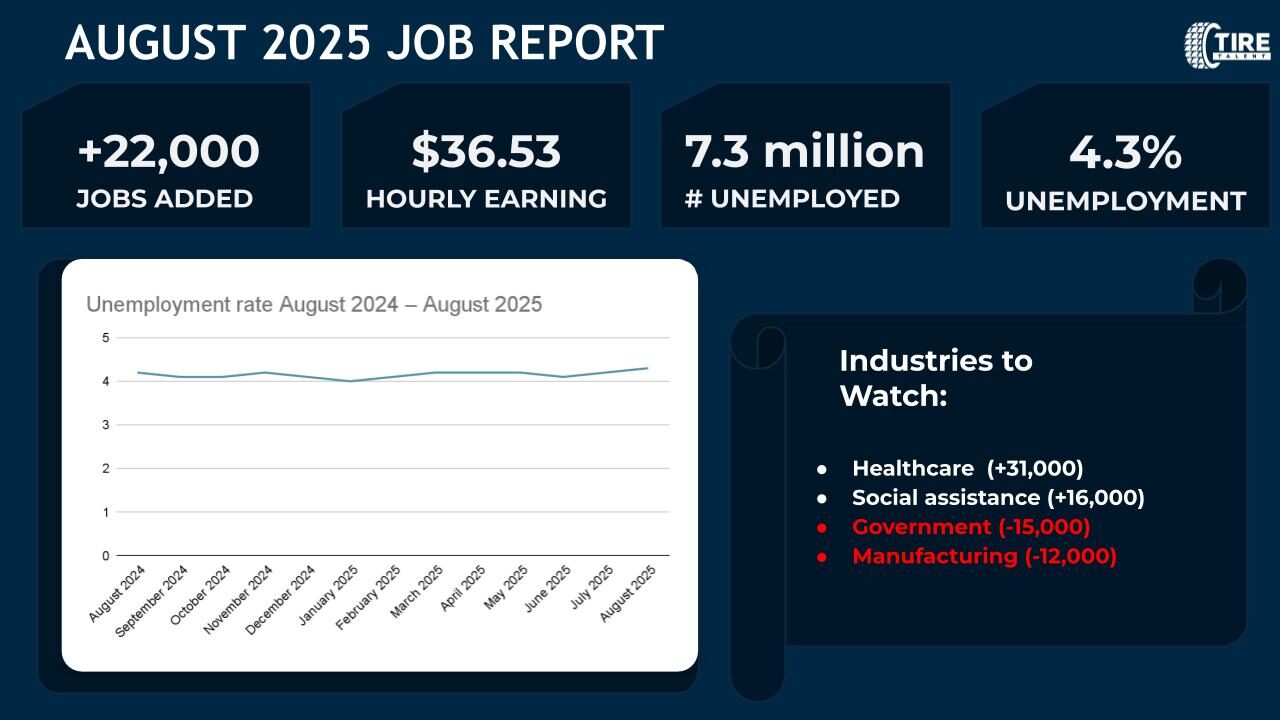
- Job boards already show many Tire Engineer roles in the U.S., with salary ranges from $84,000 to $180,000 depending on skill, specialization, and seniority.
- On aggregate, demand for engineering roles in EV / automotive systems is rising. For example, EV industry engineering roles are projected to grow ~5% between now and 2032 per U.S. BLS though not specific to tires.
These signals indicate that companies focusing on EV tire capabilities will face higher competition for talent in niche technical areas.
3. Roles & Skills in Demand for EV Tire Technology
Given the technological shift, here are roles that are or will be increasingly critical, along with skills to look for.
Role | Core Responsibilities | Skills & Domain Expertise |
Tire R&D Engineer – EV Focus | Develop compounds, tread patterns, lab testing under EV conditions | Polymer chemistry, material science, finite element analysis (FEA), heat modeling |
Smart Tire Sensor Engineer | Design and integrate sensors (pressure, temperature, wear) | Embedded systems, IoT, MEMS sensors, firmware, wireless comms |
Data / Analytics Engineer | Process sensor data, predictive models for wear and maintenance | Python/R, time-series analysis, machine learning, data pipelines |
Noise & NVH Specialist | Model & reduce noise, vibration, and harshness in EV context | Acoustics, simulation tools, materials & structure design |
Durability / Life Cycle Engineer | Accelerated life testing, degradation modeling, strength under torque | Fatigue modeling, thermal analysis, mechanical modeling |
Materials / Compounding Engineer | New rubber compounds with sustainable materials, durability balance | Polymer science, additive engineering, sustainability materials |
Tire Testing / Validation Engineer | Lab & field testing under EV conditions (torque, weight, heat) | Test design, instrumentation, sensor data interpretation |
Integration / Systems Engineer | Integrate tire-sensor systems with vehicle safety, software, and control architectures | Systems thinking, software interface, vehicle dynamics, controls |
Desired skills / experience might include:
- Experience with advanced materials, composites, and polymers
- Proficiency in simulation tools (FEA, CFD), data modeling
- Embedded systems / firmware / sensors
- Experience in battery / EV context or heavy load dynamics
- Cross-domain thinking: connecting mechanical, electrical, software domains
- Aptitude for research, prototyping, iterative improvement
Because many of these roles are novel, many candidates will come from adjacent domains (automotive, materials research, sensors) and need mentorship or domain ramp-up.
4. Compensation & Benchmark Ranges
Here are typical ranges and compensation levers for EV / advanced tire roles in the U.S.:
- Tire Engineer roles are often listed between $84,000 and $180,000 depending on seniority, specialization, and location.
- More niche roles (sensor integration, IoT / firmware) may command premium rates above baseline engineering roles, particularly in high cost regions or for rare skillsets.
- Compensation structure may include base salary + bonuses, stock / equity (especially in EV / startup contexts), and performance incentives tied to product metrics.
- Benefits, R&D environment, training opportunities, and intellectual challenge become key differentiators for top talent beyond base pay.
5. Hiring Challenges & Barriers in EV Tire Tech
Even with opportunity, there are real obstacles.
Skill Gap & Talent Scarcity
The intersection of tire engineering, sensors, data analytics, and EV domain knowledge is rare. Many candidates lack full command of all required domains.
Competition Beyond Tire Makers
Top talent in sensors, data, and materials might prefer industries like consumer electronics, medical devices, autonomous vehicles, or IoT. Tire companies must compete broadly.
Long Learning Curve & Onboarding Risk
Even candidates with parts of the stack (say, embedded or polymer) face a steep domain learning curve in tire behavior, durability, and system integration.
Cost & Time to Fill
Niche roles often remain open longer. Recruiting a smart sensor-integration engineer might take months or require global outreach.
Cross-Team Integration & Culture
Teams must integrate R&D, vehicle software, testing, manufacturing, and supply chain. Organizational silos or cultural mismatch can cause friction.
Retention & Growth Path
If roles are too isolated or advancement is unclear, candidates may depart. EV tire roles must offer clear growth into leadership, adjacent domains, or vehicle-level systems.
6. Strategies to Attract & Hire EV Tire Talent
Here’s a playbook you can use.
1. Build Forward-Looking Talent Pipelines
- Identify adjacent domains (sensor firms, IoT, materials labs) and map candidate flows
- Engage passive talent early don’t wait until role opens
- Partner with universities, material science departments, sensor labs
2. Use Executive & Technical Outreach
Messages co-signed by R&D or product leads increase credibility. Candidates want to hear from those they might work with.
3. Use Technical Assessments That Span Domains
Rather than generic tests, ask multi-domain challenges: e.g. design a sensor integration for tire pressure & forecast wear. Score not just correctness but integrative thinking.
4. Offer Learning / Stretch Opportunities
Because fully trained specialists are rare, emphasize that you’re investing in their growth and cross-training.
5. Competitive & Flexible Compensation
Use bonuses, equity, project incentives. Be ready to match counter-offers. In slower markets, offering remote/hybrid or relocation packages helps.
6. Promote Vision & Excitement
Top talent in this area wants to work on frontier challenges (range, sustainability, smart systems). Highlight that in hiring branding.
7. Onboarding & Mentorship
Pair new hires with domain experts, give them projects of gradually increasing autonomy, enable cross-collaboration with vehicle/software teams.
8. Retain with Role Expansion
Once hired, retain by allowing them to move between materials, systems, validation, or vehicle-level roles.
7. Measuring Hiring Success in EV Tire Tech
Track these KPIs:
- Time to Fill (vs average roles)
- Offer Acceptance Rate
- Quality of Hire (product performance, defect rates, test results)
- Retention at 1 / 2 / 3 years
- Pipeline Depth (candidates per role)
- Source Effectiveness (which channels produce best candidates)
- Onboarding Trajectory (time to full productivity)
8. ROI & Why It’s Worth Investing
By staffing EV tire tech roles well:
- You accelerate product innovation, bringing EV-specific tires to market faster
- You reduce R&D cycles, defect rates, and warranty claims
- You build intellectual capital (proprietary sensor systems, data models) that becomes a competitive moat
- You differentiate your brand EV tire innovation can drive marketing, position you as leader
- You avoid costly rework or mis-hires when domain knowledge is lacking
In many cases, paying a premium for top talent ends up saving multiples in development, testing, waste, and market time.
9. Example
A U.S. tire company developed a prototype “smart EV tire” with embedded sensors and predictive wear modeling. They needed 3 new roles (sensor integration, data engineer, durability engineer). Traditional recruiting gave 2 qualified resumes over 6 weeks. When they switched to proactive executive outreach, domain mapping, and technical assessment-based hiring, they found and hired 3 candidates in 8 weeks. Within 12 months, the new tire outperformed competitor models, reduced warranty claims, and served as a marketing differentiator.
10. Conclusion
The shift to EV tire technologies is forcing the tire industry to evolve materials, sensors, data, systems. Hiring demand for talent that spans legacy tire engineering and new domains is rising fast. Your success will come from proactively building pipelines, crafting technical outreach, assessing cross-domain ability, and creating roles that grow.
If you’re looking to build a team for EV tire innovation from sensor integration engineers to materials scientists Tire Talent can help you map, recruit, and onboard the talent you need. Reach out to accelerate your EV tire roadmap.